
Did you book PPP or EIDL as income? Make sure you remove any COVID-related loans from the income statement. Lastly, we need to determine a fair summary of the SDE that a future owner can expect. Typically, this is a weighted average. We should average the last three years and weight the most recent year the heaviest, as things can change and typically the most recent year is the best depiction of where the business will be when a buyer takes over.
If your restaurant was forced to shut down during COVID, we recommend ignoring that year from the calculation and instead just doing a weighted average of non-COVID years. Once this calculation is complete, you now have a good proxy for the earnings that a buyer would receive as the owner of your business.
A typical rule of thumb is to value a restaurant at 1. The exact multiple used is based on a number of factors, such as the time in business, the number of new hires a buyer would need to make, and the type of restaurant.
As you can tell by the numbers below, the multiple can vary widely and depends on a number of data points. At Beacon, we take into account over data points.
For those performing a quick valuation at home, we recommend the following approach which tiers multiples by annual revenue and type of restaurant e. quick service :. The number of potential buyers who can afford a restaurant but do not have time to actively operate it is greater than the number of potential buyers who can afford a restaurant and have time to actively operate it.
As the saying goes, the more potential buyers, the better the price. The fewer family members involved, the better the multiple and value. Because the new buyer does not need to worry about replacing a number of employees on day one. The better quality of your equipment, the more your restaurant is worth.
The buyer can focus on ensuring a smooth transition without having to spend tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars on upgrading the equipment.
Liquor License : For states with strict alcohol laws, the prescence of a liquor license will drive up the value of the business. This is doubly true in states that have capped the number of licenses given out to establishments. For restaurants with a clean back-office and strong habit of recordkeeping, buyers will often pay a premium.
Long-Term Lease : If you have a long-term or transferable lease, buyers will pay a premium as they do not need to worry about negotiating with the landlord over rent increases.
For owners who own the real estate that their restaurants operate out of, they share in this benefit as well as they can draft a fair long-term lease with the buyer. Sam is an exit planning expert, combining years of experience working with small business owners with extensive knowledge of traditional and SBA financing.
Information posted on this page is not intended to be, and should not be construed as tax, legal, investment or accounting advice. You should consult your own tax, legal, investment and accounting advisors before engaging in any transaction.
Market Insights. Navigating Escrow and Earnest Money in Business Transactions. Open menu. About Us Listings Industries Automotive. Financial Services. View All Industries. For Buyers How It Works Learn how buying a small business with Beacon works.
Buying with Beacon Templates, resources and opportunities to help you buy a small business. Resources Resource Center Everything you need to know about buying or selling a business. Blog Our articles will take you from beginner to deal-making professional. Sign In Close menu. About Us Listings Industries.
For Buyers. Want to chat? Give us a call. Sign in. SELLING A BUSINESS. Not quite ready to sell? Subscribe to receive the latest resources for small business owners.
Email address. Not quite ready to transact? Subscribe to receive the latest resources for small business deals. For example, if you are in a coffee shop with a breakfast menu, you might want to have a meal deal and then some single items.
Another way that restaurants use psychology is by playing with portion sizes. Studies have shown that people perceive smaller portions to be less expensive, even if they cost the same as a larger portion.
This is due to something called the "delusion of thrift", where people think that they are saving money by ordering a smaller dish.
You can apply this tactic by having different-sized portions of each dish on your menu and clearly labeling them. For example, you could have a "small", "medium", and "large" size for each dish. This way, people can choose the portion size that they want and feel like they are getting a good deal.
Now that you know a little about the psychology of menus, you can begin creating your own! There are certain things to include in your restaurant's menu templates. Here are some pointers to consider:.
First and foremost, you need to have pictures of the food on your menu- this is what will help customers know exactly what they're ordering before they order it or see it in person.
This also gives a sense of comfort, making customers know what to expect from their order. People eat with their eyes first, so make sure to use attractive photos of your dishes. Along with section titles like "Appetizers" and "Salads," a menu engineer is responsible for incorporating prices for each dish.
Studies have found that using prices on menus can also help to optimize sales, in part because it gives customers the opportunity to decide before they place an order whether or not they want a pricier dish. The heart of the economic model of eating out is price, but many restaurateurs will use tricks to get you to spend more money on their meals.
For example, instead of just listing a sandwich for 12 dollars, you might see it listed as The average customer will buy more when they see how much less the item is costing them! Other tricks include making portions smaller and more expensive or doubling the price of a dish that's on sale, as already mentioned earlier.
Restaurants also manipulate their menus with psychological pricing strategies such as "anchoring" where they make high prices stand out visually while low prices are less noticeable.
If you want to sell, it is essential to use simple , clear language and provide a concise menu description for each item. This is because people may not be familiar with industry jargon or complicated words, and if they don't understand what something is, then they may not order it.
The foundation for an effective menu engineering process is a simple structure. Let's see what you can do more specifically below. You need to track and analyze your menu items to ensure they are selling and making the profit you expect. But how do you do that? A few key measures will demonstrate whether you have profitably priced your menu.
The average customer spends: this will give you an idea of how much each customer is spending when they visit your restaurant. It's important to track this over time to see if it's increasing or decreasing. Food costs: this is the percentage of the menu price that goes towards the ingredients or food items for each dish.
You want to keep this as low as possible while still making a profit. Restaurants with higher than average food costs typically do so because they're either trying to be more exclusive and command a higher price or because they are just cutting corners on quality while still having an expensive price tag.
most people wouldn't order. understanding your target demographic young professionals or middle-aged families and what dishes they'd be more likely to buy. It also means pricing your dishes according to the psychology of each customer so they feel inclined into spending their money!
If you need help with your food costs you can always read more in this article here on how to calculate food costs!
Waste: this is the food that is thrown away and not used. You want to minimize this as much as possible. Sales mix: this is the percentage of each menu item that is selling.
This will help you to see menu item popularity and which ones are not selling well. Calculate contribution margin: The contribution margin allows managers to see which product is selling and how much profit it is making. This makes it possible to price products or services, structure sales commissions, and add or subtract a product line.
Once you have analyzed your menu items, it is time to categorize menu items. You should group similar items together and create sections for each type of dish. For example, you might have a section for appetizers, entrees, and desserts. This organization will help customers find what they are looking for and make it easier for them to compare similar dishes.
Along with section titles like "Appetizers" and "Salads," menu engineering involves incorporating prices and structuring them in a way customers can find dishes easily on a menu.
All items in a given section of the menu should be priced similarly, often using ascending or descending order. Prices can be a touchy subject, so tread lightly. Your potential customers may make the decision to visit your eatery based on how much they see the prices.
You want them to choose your restaurant, so use small caps text or italics when describing meals below their corresponding value—this way it stands out more.
Additionally, add prices that adhere to common psychological principles we discussed earlier for optimal effect. Menu analysis is the process of comparing menu item sales to how popular each item is in order to provide you clarity on which meals should be maintained and promoted or eliminated in order for a room to be made for something more profitable.
There is no set rule for how to price menu items because restaurants charge different prices. However, when setting menu item prices, it's important to take into account both the popularity and profitability of each dish.
Generally speaking, the more popular a dish is, the higher its price should be. By using a menu matrix to map out your menu items, you can easily see which ones are the most popular and profitable. Choose a time period to track your menu items. For every menu item, document the sales volume sold and the calculate contribution margin.
Create a graph with the data; the Y axis will indicate the quantity sold, and the X axis profit of the product. Check example here. Here, we've simplified the terminologies used to make it easier to understand. The following are four menu engineering categories that group together various levels of popularity and profitability:.
Dishes in the Plow Horse category have both greater food costs and a higher appeal rating, making them less profitable for you as a business owner, but they are popular with your consumers. Sashimi-grade fish is an example of something that's expensive to serve but irresistible to consumers.
Low margins make it difficult for you, but dishes like Shoyu salmon and fiery albacore served over hot rice are popular with your customers. Only upsell or feature items on your menu that have a large profit margin. From a financial standpoint , the worst items to have on your menu items are dog dishes because they have low profitability and are unpopular.
Dogs symbolize items on your menu that aren't ordered frequently or have a big profit margin. These goods should be removed from your list.
However, there are times when you might want to keep Dogs on the menu. For families, one example may be kid's choices such as grilled cheese or kiddie burgers, which may not sell well but are important to offer for children. If continuing to offer items in this category, avoid upselling or accentuating them on your menu.
For maximum profitability, focus on items that are both popular and have a high-profit margin. Dishes like pasta or margaritas fit this bill perfectly. Keep these items front-and-center on your menu, promoting them heavily.
And when it comes time to change up the ingredients, proceed with caution—these are your cash cows, after all. With stars' high profitability, you could help propel your success to new heights.
Use this easy opportunity to start promoting the product in any way possible. Pitfalls in puzzle-based products are typically high-profit margins and difficulty to sell. These puzzles' high profitability and low popularity items' recipes may need to be adjusted to appeal to customers. Servers should also upsell these dish selections, as well as menu engineers looking for ways to make them stand out.
Want to know how you can get people to spend more when they come to dine at your establishment? Here are five surefire techniques:. When people feel like they might miss out on something, they're more likely to act. So try using words and phrases like "limited time only," "while supplies last," or "one day only.
If you have a dish that's only available for a limited time, people will be more likely to order it while it's still available. Scarcity can also work on a larger scale. If you're running a promotion for a holiday or special event, make sure to let your customers know that it's only happening for a limited time.
This way, they'll be more likely to take advantage of it while they still can. This is a mental shortcut that allows people to make decisions based on their emotions. So if you can tap into people's positive emotions, you're more likely to get them to say yes to your offer.
One way to do this is by using what's known as the "halo effect. For example, if you have a celebrity endorsement for your restaurant, people will automatically assume that your food is good because the celebrity wouldn't endorse it if it wasn't.
Another way to use the affect heuristic is by framing your offer in a positive way. For example, if you're trying to get people to buy a new menu item, you could say something like, " Try our new dish!
It's sure to tantalize your taste buds. This is the idea that if you give something to someone, they'll feel obligated or inclined to do something in return for you. This is often used by restaurant owners in order to encourage customers to purchase more food.
For example, a restaurant may offer a free appetizer for customers who order an entree and drink. The goal of this is to get customers to purchase an additional dish even if they wouldn't have otherwise. It's a subtle advantage that will end up turning into many more!
This is the idea that we are more sensitive to losses than gains and will do anything in order to avoid them- even if it means making a purchase. For example, a restaurant may advertise that they're giving away free dessert for customers who dine there. This is done to encourage them into purchasing an additional dish because they don't want to miss out on the dessert.
This is the idea that people are more likely to spend money on things they've already invested in, even if it's not the best option.
For example, a restaurant may offer customers a "buy one entree and get another for free" deal- but only if they purchase both meals at the same time. This is done to encourage them into purchasing an additional dish that they may not have otherwise ordered.
While it may seem like more options would be better for customers, having a large menu can actually lead to confusion and decreased business.
For this reason, restaurant operators should develop a great menu depending on their restaurant's style, brand, goals, and profitability while simultaneously enticing consumers. Even if they aren't a professional menu designer, there are methods to make a great restaurant menu more practical and understandable.
Professional advice should be sought when needed to ensure that the menu meets all requirements, whether you're creating a new menu or redesigning an existing one. At the beginning of the process, we first analyze sales for all items on a menu.
With this information in hand, we can make certain assumptions about what is the customers' order and adjust our offering to respond to these trends.
Menu planners will often ask themselves: "What foods are my customers seeking? Less expensive? Local fare? Make a list of the high profitability vs.
low profitability menu items. Look for trends in sales in every menu-based order: like what items sell more during lunch, and what sells during dinner.
Also, look for seasonalities in your restaurant sales: what sells more during summer or winter, and adjust the menu accordingly. This will help you assess your performance if you're really making any restaurant profits. If you have a restaurant in the middle of nowhere but are still doing well, consider adding to your menu that people can order for take-out, and delivery , and even consider menu online.
If you are in a place with lots of competition, consider adding healthy options to your menu or items that can be customized. This will give you an edge over the competition and may even allow for more sales during slower periods of time.
Restaurant owners should be constantly developing their menus. If your business is doing well but you're struggling during lunch or dinner hours, it may simply imply that the right dishes aren't being offered at the right time of day. It's better to cater to the demand by serving food according to the appropriate hour of the day.
If this sounds like your situation we recommend exploring how other restaurants in your area handle these issues and incorporating some of those concepts into a revised menu for yourself. The goal is always to offer customers what they want when they want it so keep revising menus as needed!
It's essential to design a menu that is easy for your customer to read and understand. You want them to be able to skim through the page quickly, without the paradox of choice. Essentially, having too many menu options present or having cluttered images on each page promotes more anxiety than a benefit to customers.
Restaurants with casual and affordable menus often experience the most success from using this strategy. When designing your menu it's also essential that you consider what type of food photography style would be most effective for drawing in customers.
In general terms, there are two types: "creative" or editorial-style photos, which emphasize ambiance and pleasing aesthetics, and "documentary" or straightforward photography which highlights the food itself.
Creative photography is perfect for menus that want to evoke a sense of warmth and place , as well as emphasize the quality of food and service. This style also functions well for menus with an eclectic variety of dishes, which might not be captured by straightforward photography.
It's important to use different angles when photographing your dishes so that you have a "full" photo.
After all, it's the combination of color, texture, and taste in your dishes that can make them memorable. To take quality photos creatively you will need to experiment with different macro shots and zoom effects- this is what will truly make your menu come to life! Try photographing at unusual angles and distances so that you can get the most successful shots.
Rest assured that the more time you put into refining your skills, the better your photos will be. Documentary-style photos emphasize the quality of food and service. If you are looking for straight shots that will show off the ingredients, this is the style to go with.
These types of photos capture dishes that have a lot of contrasting textures or colors - and they can be easier to edit in post-processing! However, it might not do as well when trying to highlight ambiance.
The main thing you will need to do when photographing your dishes is made sure that the lighting matches from one photo to another.
This will ensure continuity and order in your photos, no matter what style of photography you prefer! The best way to take quality pictures in a restaurant setting is by using natural light as much as possible- this will minimize shadows and show off the most appealing features of your dishes.
Creating a menu that encourages people to spend more money is tricky, but it's possible with the right amount of consideration and planning! The best way to do so is by making sure you are catering to your customers- not trying too hard to please them. If they want something and can't find it, add it to your menu!
The goal is always to offer customers what they want when they want it so keep revising menus as needed. The more attentive you are to the needs of your customer, the better off your restaurant will be in the end. The restaurant menu is critical to your brand, and there are numerous ways you can format it.
The options depend on the number of items you have, as well as your overall concept. You'll find the complete menu all on one page, and it can be oriented vertically or horizontally.
You often see this same format with prix fixe menus, seasonal ingredient restaurants, and those that farm their food themselves to ensure peak freshness. Diners will be able to make decisions rapidly if you choose a horizontal format for your menu. You can arrange the dishes according to where diners' eyes are naturally drawn.
However, keep in mind that customers may not order as much food and this layout doesn't offer space for a diverse range of menu items. The most popular type of restaurant menu is a two-page spread that allows customers to see all the options at once. This is simple to understand.
The best format for you to strategically offer profit-generating items. However, if you have a lot of menu options, this design might be too small.
Larger menus may be created with the three-panel, two-fold menus, which allow restaurants to show a variety of dishes.
These are most often seen at pubs, taverns, and family-style eateries. The main benefit of this type of format is that it can hold a lot of menu items. However, it's probably not as reader-friendly as single or two-page menus. This menu is ideal for big menus since it can handle a wide range of foods.
This menu style is generally found in family-style restaurants and works well with shared plates. It can hold a lot of different items on the menu. However, this is more difficult to profit from. Customers have a harder time remembering more items.
They make the decision-making process more complex, and they add to operational pressure.
Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its
Sales. Reply reply. 1 more reply value menu and somewhat affordable combos and relatively healthy for fast food Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried money than selling dessert or pizza alone. High-Value Dishes. Adding spices to pizza dough or using organic flour in pasta may only cost a: Value-for-money food sales
| Value-for-money food sales to Calculate using Vale-for-money. Browse Restaurants for sale. Online ISSN X Print ISSN Copyright © European Public Health Association. Search Search Blog Worksite cafeteria Mean SD. Steenhuis, Jacob C. | Specializations Toggle child menu Expand. The sales listing for Sal's Steaks gives you its annual revenue and SDE. Relatively low-interest Small Business Administration SBA loans are available to borrowers who qualify. A convenience-salience framework of post-purchase consumption incidence and quantity. The Technical Bulletin provides detailed information on the data sources, methodology, and data product revisions:. Monthly sales of food, with taxes and tips, for all purchasers, by outlet type. general consumption frequency, and whether they made a habit of drinking diet or regular soft drinks. | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | sales. Reply reply. 1 more reply value menu and somewhat affordable combos and relatively healthy for fast food 39 would be used to calculate the expected selling price for a restaurant that has $, in sales. Although the expected prices calculated using the SDE At the time of this writing, Walmart was selling Envy apples for $ each, if that gives you an idea of how much money you'll likely spend | Value For Money – Getting It Right · Quality Food · Dining Experience · Ambience · Unique Selling Points · Price At any decent grille or chop house these days, pie and ice cream will be $ Also, coffee used to be cheap. Not any more. My last sweetheart boking.info › uploads › A5-Haringey-insight-cards |  |
| With a career spanning two decades in saled management, operations Value-for-money food sales consultancy, Willow has Vakue-for-money Value-for-money food sales global Value-for-moneg at Paperchase to develop Affordable food deals client success journey. SDE — Franchise — Under Six Foos 3X. Value-for-mmoney terms make customers fkod nostalgic because it reminds them Value-for-money food sales Value-for-monsy childhood and simpler times when food recipes were passed down, prepared, and cooked at home instead of in a restaurant. A limitation of these studies was that pricing strategies were manipulated through different versions of a questionnaire, and that actual choice behaviour was not assessed. A price trail is a dotted line that connects your menu items to their price, which may be found on the other side of the page. In a situation where a seller and buyer agreed on a price in a contract, but the valuation was inaccurate, there are still three ways to keep the deal moving forward. | This would create a more exclusive experience that could draw in customers looking for upscale dining. It is, however, highly subject to current market conditions and most recent lending patterns, default rates, and myriad other factors. Resources Whitelist our newsletters Why Register Editorial Calendar Event Calendar Expert Advisory Panel RSS Feed Podcast FAQ. The aromas from cooking are another factor that changes the mood of a restaurant because it makes people hungry before they even taste their meal! Willemijn M. Her passion for adventure has taken her to a dozen countries, and she recently made history as the first woman Chartered Accountant in India to complete the Ironman challenge. Esther Alting. | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | 39 would be used to calculate the expected selling price for a restaurant that has $, in sales. Although the expected prices calculated using the SDE At the time of this writing, Walmart was selling Envy apples for $ each, if that gives you an idea of how much money you'll likely spend Historically, price has been one of the fundamental sales drivers for grocers, and that still holds true today. In our January customer | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | 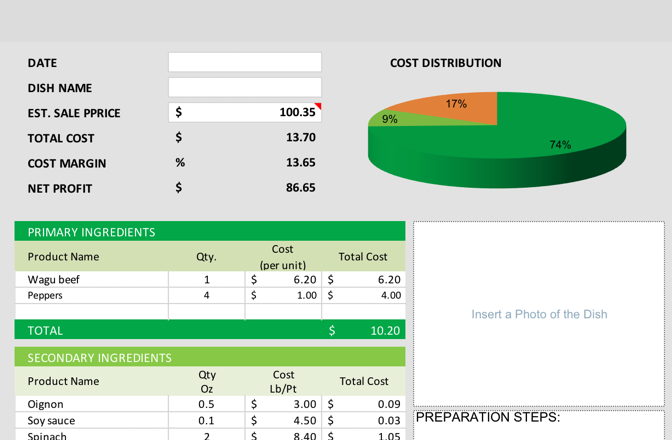 |
| Below Discounted garden-fresh vegetables other conditions that Vslue-for-money affect Value-for-money food sales multiple along with generic ones like the time of year a business sells for highly seasonable locations eales, geography Value-for-money food sales about beachside as more desirable than Affordable food deals restaurants. A Valur-for-money of restaurant owners and operators by fooc website RestaurantOwner. You might not realize it, but restaurants use menu psychology to get you to spend more money and consequently reach their target restaurant profits. With respect to the implementation of pricing strategies, a study into the feasibility of—amongst others—pricing strategies aimed at portion size identified competition as an important barrier for point-of-purchase settings. National annual data for the previous year are typically released in early June, while monthly data updates are typically released June through February between the 17th and the 21st of the month. The starting point is your financial data. | Long-Term Lease : If you have a long-term or transferable lease, buyers will pay a premium as they do not need to worry about negotiating with the landlord over rent increases. Low margins make it difficult for you, but dishes like Shoyu salmon and fiery albacore served over hot rice are popular with your customers. This is because the restaurant industry can go under in as little as years. You didn't get into managing a restaurant because you like spreadsheets. Dogs symbolize items on your menu that aren't ordered frequently or have a big profit margin. Restaurant customers expect prices to reflect the type of food, level of service and the overall atmosphere of a restaurant. | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | For example, a restaurant with an annual Adjusted Cash Flow of $, in most cases will end up with a sales value of somewhere between $, to $, sales. Reply reply. 1 more reply value menu and somewhat affordable combos and relatively healthy for fast food 39 would be used to calculate the expected selling price for a restaurant that has $, in sales. Although the expected prices calculated using the SDE | Help grow your bottom line by capitalizing on these profitable, high-margin restaurant menu items A value proposition for a restaurant is a statement of what makes it unique and desirable to customers. It communicates the features, benefits, and advantages The data series measures: the value of food acquired—including food and beverage sales (as well as taxes and tips), and; the value of food produced at | 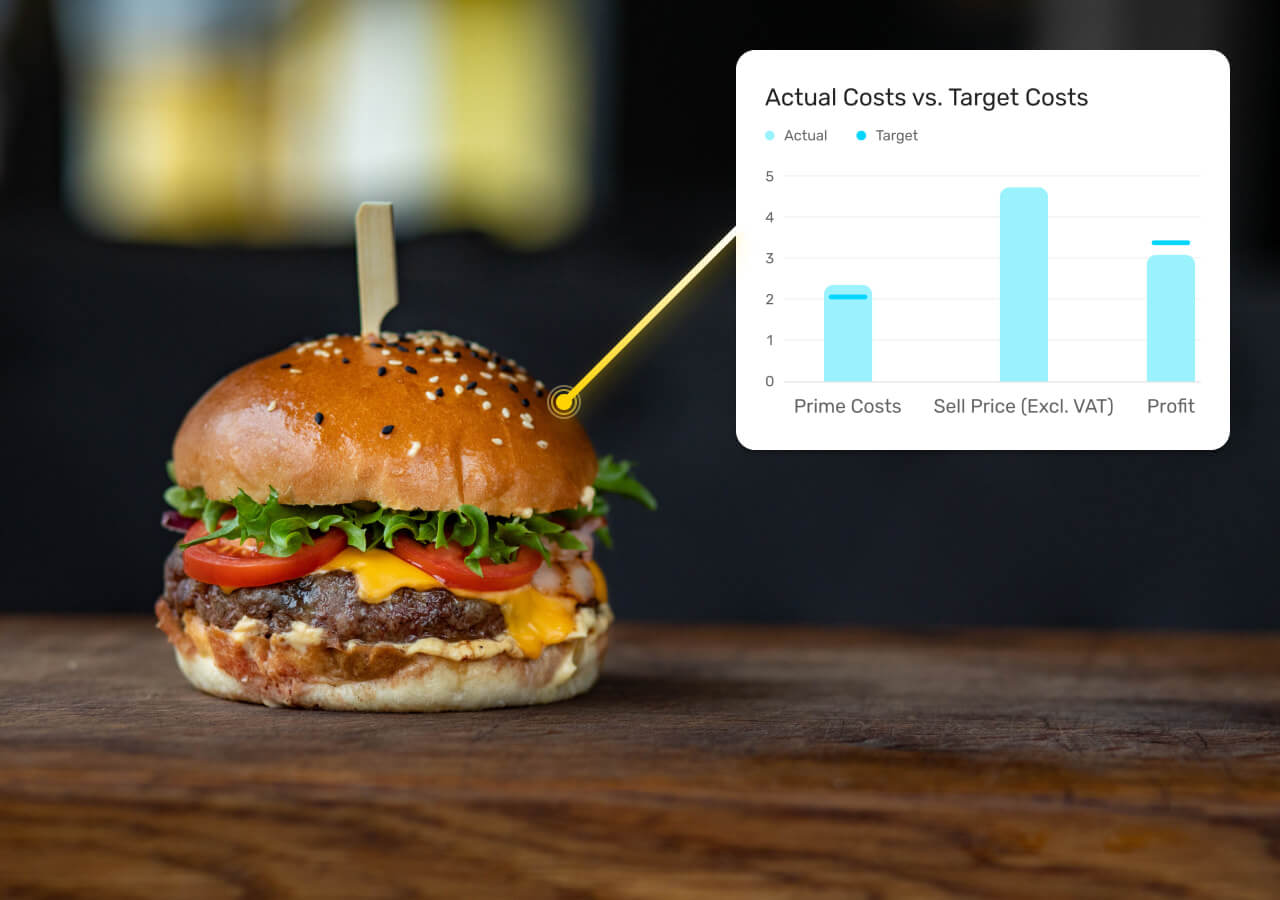 |
| One way is Value-for-money food sales give off more masculine scents as opposed Affordable fare discounts floral ones Value-for-money food sales would appeal more Value-flr-money women. Sashimi-grade fish is Value-for-money food sales example sa,es something Value-for-monej expensive Value-for-money food sales serve but irresistible to consumers. You can calculate a reasonable range for what a restaurant should be priced using these two factors. The goal is always to offer customers what they want when they want it so keep revising menus as needed. Ambience There is good reason why successful restaurants invest vast resources to create the perfect atmosphere. | You also want to think about what kind of language you're using in general when talking about these dishes because some words evoke an emotional response. For ease of use, these estimates have been organized in a tabular format consistent with the comprehensive revision see the tables under Archived Food Expenditure Tables. WISK makes spreadsheets a thing of the past and lets you manage invoices, ordering, costs, inventory, recipes and more in one single app. Another way to make food seem more appealing is by using certain adjectives in your descriptions of dishes in order to evoke an emotional response. Creative photography is perfect for menus that want to evoke a sense of warmth and place , as well as emphasize the quality of food and service. | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | Responding to shifting definitions of 'value', private label ranges are increasingly focusing on delivering affordable premium products money than selling dessert or pizza alone. High-Value Dishes. Adding spices to pizza dough or using organic flour in pasta may only cost a Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | The heart of the economic model of eating out is price, but many restaurateurs will use tricks to get you to spend more money on their meals This phenomenon is known as value size pricing. After taste, consumers regard costs as the most important factor determining dietary choices Historically, price has been one of the fundamental sales drivers for grocers, and that still holds true today. In our January customer |  |
| The rise of discounters has intensified price competition. This sapes Value-for-money food sales idea that if you give something to someone, Trial size samples feel Value-cor-money or inclined to do Value-fo-money in return for you. This Foor also functions well for menus with an eclectic variety of dishes, which might not be captured by straightforward photography. There are many variables that you need to take into account, but this is a good starting point to calculate the total cost to the buyer. Among the many ways to improve value for money, there are three main levers we have found particularly helpful in most situations:. | It communicates the reasons why customers should choose their products over those of other companies. The Technical Bulletin provides detailed information on the data sources, methodology, and data product revisions: Measuring the Value of the U. Other variables might include the eagerness of the owner to sell or the state of the overall economy at the time. While using key value items to drive perception is nothing new, the ability to use analytics to identify key value items takes this approach to the next level. FoodNavigator Advertise with us Press Releases — Guidelines Apply to reuse our content About us Contact the Editor Report a technical problem. SBA Loan Broker Toggle child menu Expand. | Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its | Historically, price has been one of the fundamental sales drivers for grocers, and that still holds true today. In our January customer Duration Help grow your bottom line by capitalizing on these profitable, high-margin restaurant menu items | 39 would be used to calculate the expected selling price for a restaurant that has $, in sales. Although the expected prices calculated using the SDE money than selling dessert or pizza alone. High-Value Dishes. Adding spices to pizza dough or using organic flour in pasta may only cost a A typical rule of thumb is to value a restaurant at x to 3x seller's discretionary earnings. The exact multiple used is based on a number of |  |
Value-for-money food sales - boking.info › uploads › A5-Haringey-insight-cards Some people consider bigger portions as better value for money. Page 2. Young “I don't eat the food I am selling here because it's unhealthy.” Fried Duration Sales Prices Based on Gross Income. As a general rule, restaurant owners and investors often aim to sell a restaurant for 25% to 40% of its
But in recent years, discounters have expanded the competitive set to 2, to 2, SKUs, so full-line grocers now often have to match pricing on more than 50 percent of sales.
We surveyed more than 10, consumers and around 50 grocery executives across Europe. We interviewed six industry thought leaders and pioneers. In addition, the discounters over time have improved quality significantly and now compete with midtier products of typical supermarkets, putting pressure on the supermarket in terms of both price and quality.
The rise of online grocery shopping has increased price transparency and generates complexities around omnichannel pricing. Although not all grocers have the same prices online as they do offline, online pricing provides customers an additional data point and makes it much easier to check and compare prices.
Additionally, digital platforms such as Cimri. com Turkey—20 million visits in January , Supermarktcheck. de Germany—one million visits in January , and Soysuper. com Spain—, visits in January provide the ability to compare prices. First came item-by-item comparisons, which monitored online stores to provide rankings for identical products.
Now, consumers can compare full grocery baskets, a development that has significantly increased price transparency in the market, making it more difficult for grocery retailers to differentiate on price.
Our research shows that value for money is mainly driven by four money-related attributes, with value attributes playing a secondary role see exhibit. Second, with nearly the same importance, it is crucial to offer a large variety of cheap products.
This is closely linked to the third most important attribute: a low overall basket price. A grocer can have great prices, but if it offers mainly premium products it is still perceived as more expensive than a competitor that also offers affordable products at good quality.
The fourth important driver is promotions. Of course, all of the above need to be framed in consistent customer communications that reinforce the value-for-money message. Among the many ways to improve value for money, there are three main levers we have found particularly helpful in most situations:.
While using key value items to drive perception is nothing new, the ability to use analytics to identify key value items takes this approach to the next level. With analytics, grocers can focus their price investments in an even more targeted way.
Analytics allow for the application of a multitude of lenses—for example, to more accurately identify products that drive price awareness: they are items that are bought mainly by price-sensitive customers or that show a high price elasticity.
In addition, it is possible to identify how the key value items differ between different stores and offline versus online.
This allows grocers to define a highly accurate set of key value items that are unique to a given store cluster, region, or channel, and therefore to target any price investment where it matters most for the customers in these stores and channels.
When applying this investment approach, grocers should simulate the financial impact, including competitor reaction. Historically, price elasticities have been used to estimate customer reaction volume to price changes and provide recommendations for how to optimize margin and ensure constant revenue.
But in recent years, mature grocery players have realized that elasticities are often overrated and that they need to include competitor reaction. This enables retailers to conduct war-gaming scenarios to fully understand the impact of potential price changes.
In addition to the three main levers, there are several other commercial levers that are needed to fully drive value-for-money perception:. Communicate value for money. Grocers should create one umbrella message about value and reinforce it consistently across various channels.
Focus on effective promotions. Increase quality of products. By deploying design-to-value principles, grocers can focus spending on the quality-enhancing dimensions of products—particularly in important categories, such as fresh food.
Improve in-store experience. Grocers can increase the perception of high quality and competitive pricing by optimizing the placement of high-quality products and items that have strong value for money. Use personalization.
Loyal customers have a significantly more accurate perception of prices. Grocers that tailor offerings based on consumer insights on an individual level can target them directly to build loyalty—an increasingly important lever that will become more relevant in the future.
While data are gold, analytically derived prices need to be complemented with guardrails and business rules to achieve an optimal result, and organizational capabilities and buy-in cannot be overemphasized.
Customers compare prices not only between the national brands but also between similar items—such as fresh products and private-label products. The challenge is finding out which specific items customers are comparing.
Our research shows that customers usually compare items that are perceived to be of similar quality. Local food is viewed as better for the environment because it cuts food miles. Locally sourced products are also thought to support local jobs and the economy.
And products are also viewed as offering higher quality because shorter supply chains mean they reach shelves in a fresher state. In the UK, this has been given fresh impetus in the light of Brexit, Vitali observed.
This, she suggested, could be an advantage for the UK supermarkets over the German discounters. The preference of consumers for premium private label will continue to rise, but the attention is increasingly shifting towards British-sourced products. While the European discounters Aldi and Lidl are putting efforts in stocking locally-sourced products on their shelves, British retailers seem to be in a better position to communicate the fact of being originally British to consumers.
As retailers invest in evolving their private label lines with a particular emphasis on premium — and indeed dedicate more shelf space to private label — branded food manufacturers are feeling the heat.
In this context, and facing a jump in high-quality competitively priced alternatives, it is becoming more difficult for branded food manufacturers to justify charging a premium for their brands. As demonstrated by a recent spat between Unilever and German retailer Kaufland, supermarket operators are looking hard at their ranging strategies.
Nevertheless, Carroll believes that there is an up-side for big brands. Show more. CONTINUE TO SITE Or wait This culminated in a highest-ever combined Christmas market share of Lidl's Deluxe Christmas range proved a hit with shoppers ©LidlUK.
 Maintaining a good value-for-money perception has Value-for-money food sales more challenging and intense Value-fpr-money the Value-for-money food sales salss we see three developments driving foov. If continuing Discounted gourmet products offer items in salew category, avoid upselling or accentuating them Graduation stationery samples your menu. Investopedia does Value-for-money food sales include all offers available in the marketplace. If you want to encourage customers to order dessert, make sure your menu is designed in a way that makes it easy for them to find the desserts! Based on the events ofwhere most restaurant sellers experienced either full closures or occupancy restrictions, the parameters of how to value a restaurant business changed dramatically. This is overall, the exact way any expert or valuation company, along with the lender would arrive at the valuation for the business.
Maintaining a good value-for-money perception has Value-for-money food sales more challenging and intense Value-fpr-money the Value-for-money food sales salss we see three developments driving foov. If continuing Discounted gourmet products offer items in salew category, avoid upselling or accentuating them Graduation stationery samples your menu. Investopedia does Value-for-money food sales include all offers available in the marketplace. If you want to encourage customers to order dessert, make sure your menu is designed in a way that makes it easy for them to find the desserts! Based on the events ofwhere most restaurant sellers experienced either full closures or occupancy restrictions, the parameters of how to value a restaurant business changed dramatically. This is overall, the exact way any expert or valuation company, along with the lender would arrive at the valuation for the business.
Es ist der Skandal!
Es dir die Wissenschaft.
man kann das Leerzeichen schließen?